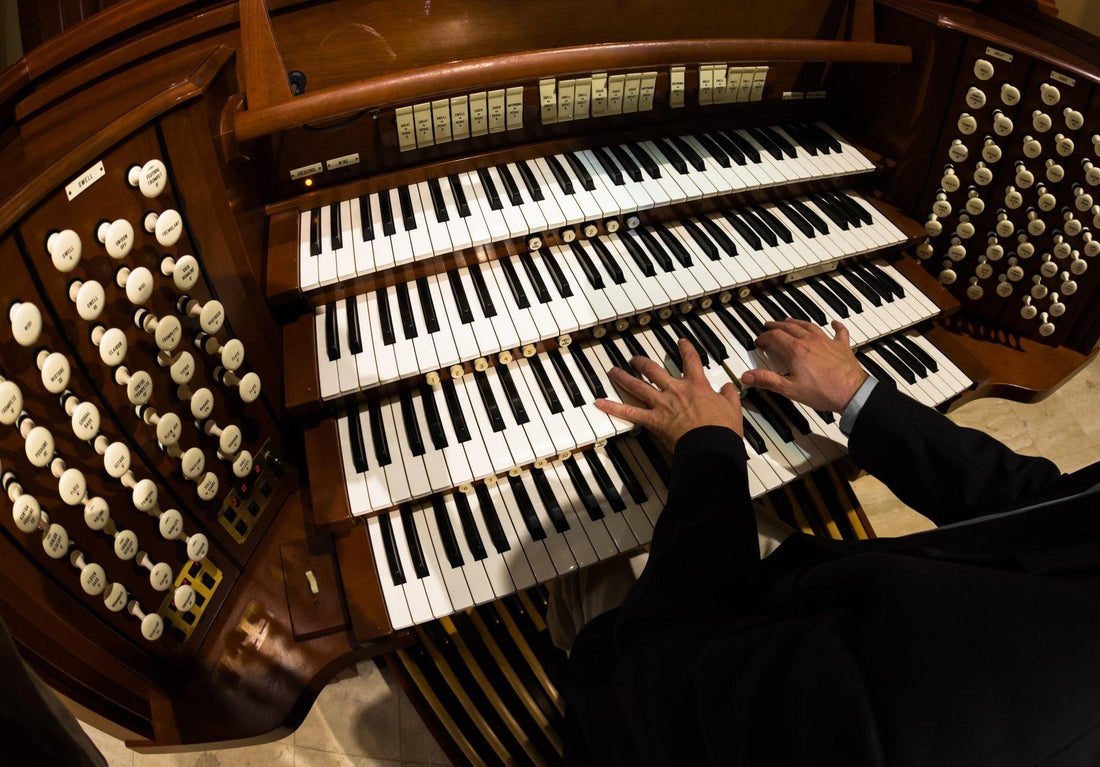

Exploring the World of Organs: Understanding Different Types and Their Sounds
Music has the extraordinary power to evoke emotions, tell stories, and create beautiful atmospheres. Among the many musical instruments, the organ stands out with its majestic sound and rich history. Whether you’re a budding musician or a passionate listener, understanding the various types of organs can enhance your appreciation for beautiful organ music. In this article, we’ll traverse through the fascinating realm of organs, exploring their types, characteristics, and the music they produce.
The Essence of Organ Music
Before diving into the different types of organs, it’s important to understand what makes organ music so captivating. Organs can create a wide range of tones and textures, allowing for expressive performances across numerous genres—from classical pieces to modern interpretations. The ability of the organ to produce chords and multiple notes at once gives it a unique place in the world of music. This versatility is one of several reasons why beautiful organ music is cherished across generations.
A Brief History of the Organ
The history of the organ dates back more than a thousand years. The earliest predecessors of the modern organ emerged in ancient Greece with the hydraulis, which used water pressure to push air through pipes. Over time, the organ evolved through several significant developments, particularly in the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, which saw the emergence of larger, more sophisticated versions played in cathedrals and concert halls. Today, organs come in various forms, each with unique features and capabilities.
Types of Organs
Understanding the different types of organs can help you appreciate the versatility and richness of beautiful organ music. Here are the primary types of organs that musicians and enthusiasts encounter:
1. Pipe Organs

Arguably the most iconic representation of organ music, pipe organs consist of a series of pipes of varying lengths that produce sound when pressurized air is passed through them. The result is a powerful sound that fills large spaces, making pipe organs a staple in cathedrals, concert halls, and performance venues. Pipe organs can be categorized further based on their mechanism, size, and design:
- Church Organs: These instruments are specifically designed for liturgical music, often featuring robust pipe ranks to accommodate a wide range of hymns and sacred music
- Concert Organs: Built for concert performances, these organs may have a more diverse tonal palette to cater to various musical styles.
- Theatre Organs: Developed for silent films and performances in theaters, these organs come equipped with additional features such as percussion instruments, making them suitable for entertaining audiences.
2. Electronic Organs
With the advancement of technology, electronic organs have emerged as a popular alternative to traditional pipe organs. These instruments replicate organ sounds electronically and can produce a variety of tones, allowing musicians to switch styles seamlessly. Here are key types of electronic organs:
- Digital Organs: Utilizing sophisticated sampling technology, digital organs capture the sound of real pipes. They often feature various presets that mimic traditional pipe organs, making them accessible for modern music.
- Keyboard Synthesizers: Often used in contemporary music, keyboard synthesizers can emulate organ sounds and combine them with other instrument sounds, providing musicians with revolutionary flexibility.
3. Harmoniums

A harmonium is a type of free-reed organ that produces sound by air flowing over metal reeds. Played with a keyboard, harmoniums are often used in South Asian music and have a unique timbre that distinguishes them from other organs. Many musicians appreciate harmoniums for their portability and ability to produce beautiful organ music in homes and performance settings.
4. Melodeons and Accordion Organs
Although they are smaller than traditional organs, melodeons and accordion organs use bellows to push air through reeds. Players can produce a distinct organ-like sound, making these instruments popular in folk music traditions. Their compact size allows for easy transportation, making them practical for outdoor gatherings and casual performances.
How Organs Work: A Deeper Look
Understanding how different organs produce sound can enrich your appreciation for beautiful organ music. Let’s explore the mechanisms behind some of the most common types of organs:
1. Pipe Mechanism
The pipe organ operates by sending air through pipes, each tuned to a specific pitch or note. When a key is pressed, a valve opens, allowing air to flow through the corresponding pipe. As the air passes through the pipe, it vibrates, creating sound. Larger pipes produce lower pitches, while smaller pipes yield higher notes. The quality and character of the sound can vary significantly based on the design and materials used in the pipes.
2. Electronic Signal Processing
Electronic organs utilize digital signal processing (DSP) to create sound. They capture and modify recorded sounds of real pipe organs or other instruments through various electronic components. The advantage of electronic organs is their ability to replicate an extensive range of organ tones, enabling musicians to customize sounds and textures to fit their musical preferences.
3. Free-Reed Mechanism
In harmoniums, melodeons, and accordion organs, the sound is generated by reeds vibrating in response to air pushed through them. When a key is pressed, a corresponding valve opens, allowing air to flow over the reed, causing it to vibrate and produce a tone. This mechanism tends to produce softer and more subtle sounds compared to pipe organs but can create enchanting pieces of beautiful organ music.
Practicing and Performing Beautiful Organ Music

No matter which type of organ you choose to play, honing your skills will deepen your understanding and appreciation for beautiful organ music. Here are some tips for aspiring organists:
1. Mastering the Basics
Start by learning the fundamentals of playing the organ, such as hand positioning, foot coordination, and reading music. Whether you opt for a traditional pipe organ or an electronic version, these essentials are key to building a solid foundation.
2. Explore Diverse Repertoire
As an organist, you have the opportunity to explore various styles of music. Dive into classical works by composers like Bach and Handel or experiment with contemporary tunes. Expanding your repertoire will enable you to appreciate different aspects of beautiful organ music.
3. Take Lessons
If you’re serious about learning the organ, consider taking lessons from an experienced instructor. They can provide personalized feedback and help you refine your technique. Online resources are also abundant, providing tutorials tailored to various skill levels.
4. Perform Regularly
Playing in front of an audience, whether small or large, can boost your confidence and improve your skills. Look for opportunities to perform at local events, churches, or community gatherings. Sharing your passion for organ music will enhance your connection to this beautiful art form.
Finding Your Unique Sound

Each type of organ has its unique characteristics and tonal qualities. As a musician, don’t shy away from experimenting with different instruments to find the one that resonates with you. The beauty of organ music lies in its diversity, and every organist can bring a unique perspective to their performances. Here’s how to discover your sound:
1. Experiment with Styles
Try playing various genres of music on your chosen organ. From classical to jazz, each style can be expressed through the unique capabilities of the instrument. This exploration will help you identify which genre resonates with you and where your strengths lie.
2. Modify Stop Settings
If you’re playing a pipe or electronic organ, don’t hesitate to explore different stop settings. Changing stops can alter the timbre and texture of the sound, enabling you to create a fuller or more subdued experience. Finding your unique sound can often involve a mix of experimentation and creativity.
3. Collaborate with Other Musicians
Engaging with fellow musicians can inspire and influence your playing style. Collaborating with different instruments can lead to innovative interpretations of beautiful organ music, allowing for a broader creative expression.
Final Thoughts: The Allure of Beautiful Organ Music
Organs are truly remarkable instruments that have stood the test of time. Whether it’s the grandeur of a pipe organ resonating in a cathedral or the intimate sound of a harmonium in a cozy setting, beautiful organ music continues to touch the hearts of many. By understanding the various types of organs, their mechanisms, and how to play them, you can deeply engage with this captivating art form. So, embrace your passion, explore new sounds, and let the world of organ music inspire you!
Silent Night Free Sheet Music Canon | Easy Organ Arrangement for Christmas
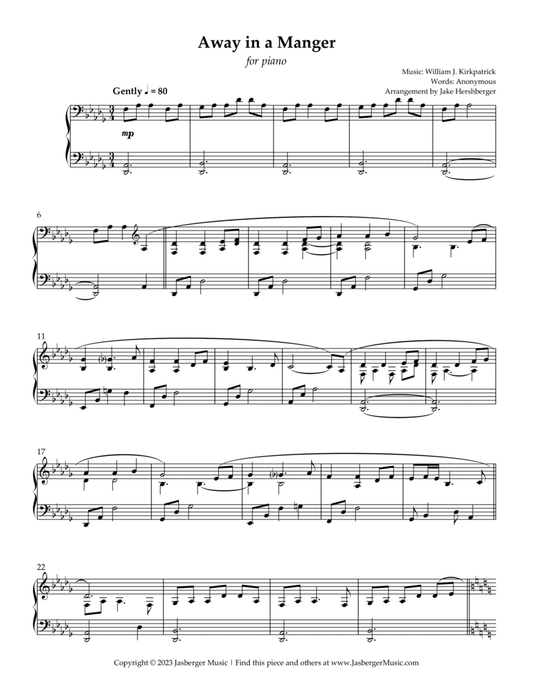
Away in a Manger Intermediate Piano Solo
Christ the Lord is Risen Today Fanfare | Easter Organ Sheet Music. For Organ, Choir or Congregation
Come Thou Fount of Every Blessing Organ Solo – A Powerful and Timeless Arrangement
View Comments
Leave a Comment
No comments



















comments